|
ANPA - National Environmental
Protection Agency
(Agenzia Nazionale Protezione Ambiente)
attention now called:
APAT - Agency for Environment Protection and for
Technical Services
(Agenzia per la protezione dell'ambiente e
per i servizi tecnici)
Legal Profile In January
1994, the Italian Parliament approved Decree n° 496 of 4 December 1993
providing for the creation of the National Environmental Protection
Agency (ANPA). This Decree became Act n° 61 of 21 January 1994.
The decision to create this Agency was a result of the referendum of
18 April 1993 which repealed the provisions giving Local Health Units
responsibility for monitoring the environment.
Thus, the Act n° 61 introduced a distinction between bodies
responsible for health questions and those responsible for
environmental control.

The National Environmental Protection Agency comes directly under the
Minister for the Environment and is subject to controls by the Board
of Auditors. Its powers, listed in Section 10(1) of Act n° 61, relate
to a series of technical and scientific activities of national
interest. Its main role is to carry out public duties, such as
providing technical and scientific backup to the Ministry of the
Environment and associated bodies with a view to protecting the
environment, the collection and periodic dissemination of data on the
state of the environment, the formulation of proposals and opinions
for both central Government and local authorities concerning quality
standards for air, water, soil, etc.
Nuclear activities are expressly referred to under the letter "I" of
the same Section which requires the Agency to exercise control over
activities relating to the peaceful uses of nuclear energy and over
the effects of ionising radiation on the environment. The Agency's
functions are essentially radiation protection inspection, as well as
formulating advice as to the legal, regulatory and administrative
provisions affecting radiation protection of workers and the public.
Under Section 1(5) of the Act, the ANPA replaces the Nuclear Safety
and Health Protection Directorate of the ENEA (ENEA-DISP), whose
functions, staff, technical structures and equipment and financial
resources are transferred to the new Agency.
In this connection, ANPA acts as the National Nuclear Regulatory Body.
The main Rule that is related to the duties and responsibilities of
the Regulatory Body is the Act no. 61 (1994).
According to the Act, ANPA has the following main duties:
- main functions of Regulatory Body,
such as the legal authority for conducting the licensing process,
for elaborating and providing the final advice for the Licences and,
thereby, for regulating NPPs siting, design, construction,
commissioning, operation and decommissioning, as specified under the
section 1-bis, comma 5 of the quoted Act
- control of the remaining activities
related to the pacific use of nuclear energy and radiations
- promotion of research on the
physical environment, pollution, industrial risks and ecosystem
protection and conservation
- systematic collection, storage and
publication of environmental data public information and
training programmes on environmental protection issues
- technical advice to public
authorities on different matters related to environmental protection,
such as :
- pollutants acceptability levels
- air, water and soil quality
standards
- waste management strategies and
technologies
Duties and responsibilities of ANPA as
Nuclear Safety Authority are better detailed in the Legislative Decree
no. 230/1995.
The main tasks of ANPA to fulfil the obligations of the Legislative
Decree n° 230/1995 are:
- controls and surveillance on
existing nuclear installations
- licensing on new nuclear
installations
- controls and surveillance on
possession, commerce, transportation, utilisation, release of
radioactive material
- controls and surveillance on
radioactive waste management
- radioprotection of workers,
public, environment
- nuclear emergency preparedness
- fulfilment of International
Agreements on control and surveillance of nuclear materials (e.g.:
NPT,
Additional Protocol)
- promotion of international
cooperation in the field of nuclear safety and radiation
protection
- promotion of actions aimed at
maintaining and improving the national know-how and the national
safety culture in the field of nuclear safety and radiation
protection
In addition to these duties, ANPA has
also to:
- support the State
Administrations to issue specific decrees for the
implementation of the fundamental nuclear laws
- to issue specific technical
guides
- to realise a National Database
on all nuclear applications
ANPA responsibilities for the licensing
process of NPPs include:
- assessment of the safety
analysis carried out by the operating organisation
- inspection of equipment and
materials during the design, construction and operational
phases for the systematic verification of plant operation
safety
- enforcement action to remedy
any failure to meet both the licensing conditions and any
safety operation criteria
The Legislative Decree n° 230/1995
foresees, in agreement with IAEA guide n° 50-C-G "Code on the Safety
of NPPs: Governmental Organisations", a Technical Commission for
Nuclear Safety and Health Protection established at ANPA.
Its role is to give ANPA an independent advice on safety and health
protection issues in relation to the main stages in the licensing
procedure and to emergency plans.
Members of this Commission are appointed by the Ministries of
Environment, Industry, Employment, Health, Interior, Public Works,
ENEA and ANPA. When necessary other specialists are appointed by the
Chairman of the Commission. For matters under the competence of other
Public Scientific Organisations and Administrations (e.g. Italian
National Institute of Health, National Research Council), in
compliance with Section 9 f the Legislative Decree 230/1995, those
Organisations and Administrations are invited to sit in the Commission
through a designated representative.
During the licensing process ANPA perform its independent assessment
on the basis of documentation presented by the licensee and involving
the above mentioned Commission.
ANPA transmit its assessment report to the Minister of Industry who
involves other Ministries. Any comment by other Ministries is returned
to ANPA to be incorporated in the final report for the Ministry of
Industry. A simplified scheme of the relationship between Authorities
having responsibility on nuclear safety and operators is shown on the
enclosed next figure.
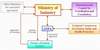
Within ANPA, while the overall
responsibility rests to the Chairman and to the General
Director, the duties of Regulatory Body are carried out by
the Department of Nuclear Safety and Radiation Protection.
At present, about 60 specialists (of which 26 acting also as
inspectors) belong to the Department, which is subdivided in
the following Sectors:
- coordination of inspection
and regulations
- emergency preparedness
- reactor safety
- nuclear technologies
- nuclear facilities,
radwaste, decommissioning
- radioisotopes and sources
- radiation protection in
nuclear installations
- radioactive and fissile
materials.
In addition, to the Department of
Nuclear Safety and Radiation Protection are assigned the following
inter-sectorial coordination functions:
- assistance to the
Eastern Europe Countries on nuclear safety and radiation
protection
- promotion and management
of international cooperations (IAEA, OECD-NEA, EU,
multilateral, bilateral).
The activity of ANPA, which covers the
protection of the environment in general (and not only the "nuclear"
field), is mainly financed by the central budget approved by the
Italian Parliament each year.
Within the nuclear field, funds are also collected from:
- Charging the operators,
at approved rates, for regulatory activities (at
present mainly in the areas of transport, medical
applications, and industrial use of radioactive
sources)
- Participating in the
RAM and TSO (ANPA is also the Italian TSO) activities
within the framework of the EU programmes
- Fines to operators for
violations (mainly in the area of health protection).
All incoming funds are approved by the ANPA Board and added to the
annual financial plan, which is subject to strict Government control.
At present, the state funding covers all personnel and operating costs.
Part of the collected funds are also dedicated to R&D activities in
the nuclear safety area and to the co-operation with a number of
international organizations (mainly IAEA, OECD/NEA, CCE).
Membership fees for these organisations are paid by the Ministry of
Foreign Affairs.
source: European website on
Decommissioning of Nuclear Installations
|
 The
only national site for collection of nuclear wastes in Italy,
The
only national site for collection of nuclear wastes in Italy,  The
only national site for collection of nuclear wastes in Italy,
The
only national site for collection of nuclear wastes in Italy,